The Acidity Question
Does acidity matter in aircraft oil? We experiment!
Every now and then you hear about oil becoming acidic and causing internal corrosion in an aircraft engine. Usually that goes along with the oil absorbing water and then forming acids, but I’ve always disagreed with this statement.
It’s a well-known fact that corrosion is a problem for a lot of aircraft engines that don’t see much use, but is it really acidic oil that’s causing the corrosion, or simply bare metal parts being exposed to the atmosphere? So I decided to run some testing to see what I could find about acidity and aircraft oils.
Now, think back to high school chemistry. Remember learning about acids and bases? Normally with something like water, you measure the pH to determine how acidic or basic a liquid might be. A pH of 7 is neutral, lower than 7 is acidic, while higher than 7 is basic.
The problem with oil is, you can’t run a pH on it directly. So instead, we have the Total Base Number (TBN) and Total Acid Number (TAN) tests.
These are fairly simple tests and the basic principle is this. After you mix a measured amount of oil with some chemicals, you can run a pH on those chemicals. But that doesn’t equate to the TBN or TAN.
To get the TBN you add acid to the chemical mixture until it reaches a pH of 4. To get the TAN, you add a base to the mixture (in this case, potassium hydroxide) until the pH reaches 10. (You might wonder why we don’t just report the pH of the chemical mixture and have that be the end of it, and the answer to that is unknown, at least to me.)
The TBN test
The TBN test is commonly done on automotive oils, but not aircraft oil. That’s because the TBN always reads 0 or close to it with aircraft oil.
Automotive oil has a lot of additive packed in there and that is what the TBN reading is based on. That additive makes the TBN increase. Oil salesmen use the TBN test to help sell their oil, with the idea being that the higher the TBN, the better the oil. But the TBN is really just a testament to how much additive the oil starts with, not necessarily how well the oil will work in any given engine.
You might wonder why aircraft oil doesn’t use the same additives? It’s because the additives used in automotive oils aren’t ashless. The additives present in all aircraft oils have to be ashless, meaning when the oil burns nothing is left. This is why it’s a bad idea to use anything other than aircraft oil in your aircraft engine.
The TAN test
The TAN test is commonly done on industrial oil like hydraulic fluid. There is a theory that when oil becomes acidic it will accelerate wear and cause all kinds of problems, but that’s just a theory — and a pretty weak one in my book.
When most people think of acid, they might think of something like acid reflux and heartburn. Or maybe sulfuric acid burning a hole in their clothes, but that gives acids a bad rap. If it weren’t for acid, your food wouldn’t get digested and we’d be without a lot of very important chemical compounds. What’s more, there is no known correlation between acidic oil and higher wear that I know of.
It is commonly talked about that water in oil will cause it to become acidic, and maybe it will if the water has something to react to. But with aircraft oil, it doesn’t. The additives present aren’t sulfur-based like they are with automotive oils, so when water gets into oil, it usually just stays there until the oil gets hot enough to cook it back out.
Testing the theory
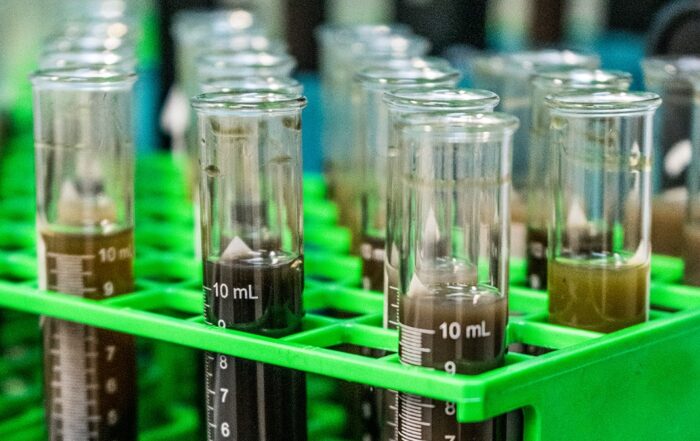
So for this newsletter article, I decided to run some TAN tests on various aircraft oils and see what shows up. Virgin aircraft oils usually have a TAN in the range of 0.4 to 0.8. It’s important to know where the TAN starts out, so you know how acidic the oil has become after use. (You’d think that oil starts out with a TAN of 0.0, but usually it does not.)
For the used oil data, we tested the TAN on 63 random aircraft samples.
The average TAN reading for those samples was 1.3. That might seem like a fairly large increase, but in the oil analysis world, 1.3 is considered a low acidity reading for any type of system. A reading of 3.0 shows some acidity and anything over 4.0 can be considered fairly acidic.
The highest TAN reading we found was 2.3, but in our testing any readings over 2.0 were rare. In fact, only three samples read higher than 2.0 and none of those had water present, but two were considered inactive. Five of the samples we tested did have a trace of water present, but their average TAN was just 1.1, so we didn’t find any correlation between water and a high TAN.
So how about inactive engines? Two samples that were inactive did have a TAN of over 2.0, but they were the exception, not the rule. We had 11 samples in our test run that were considered inactive, but the average TAN of those was just 1.2.
Based on this testing, it doesn’t look like oil acidity is really a factor at all. Does that mean you shouldn’t worry about inactivity? No — we’ve seen too many examples of poor wear from inactive engines to say that’s not a problem. What it does mean is that in our opinion you don’t need to worry about your oil being acidic. And in life, one less thing to worry about is a good thing!
Related articles
What’s the Best Oil Change Interval?
How do we determine the best oil change?
All About Insolubles
What are they and what causes them to form?
Fuel in Diesels
How often is fuel a problem in diesel engines?
Does Oil Brand Matter?
The right oil may be right in front of you.